Article
Article
How a Class II, Type B2 Biosafety Cabinet Works

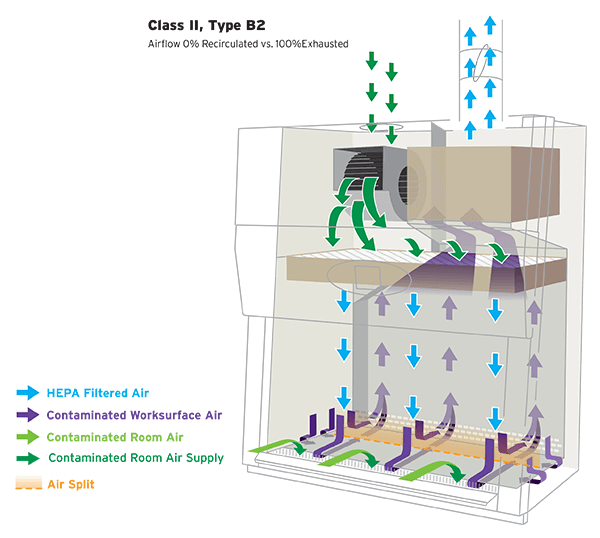
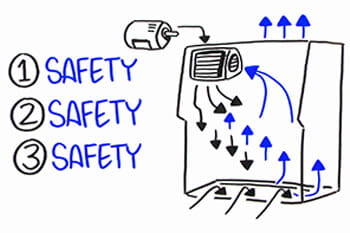
The Class II, Type B2 Biosafety Cabinet combines several key features to ensure safety and effectiveness in handling hazardous materials, especially when working with volatile chemicals or radionuclides. This type of cabinet is distinct in its operations, designed to simultaneously protect personnel, products, and the environment. As part of the broader family of Class II biosafety cabinets, the Type B2 model is uniquely engineered for total exhaust operation with no internal air recirculation.
How a Type B2 Cabinet Protects Personnel, Product, and the Environment
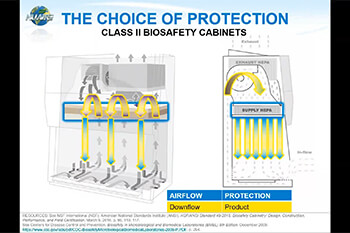
Airflow Path and HEPA Filtration in a Class II, Type B2 BSC
In a Type B2 cabinet, inflow air enters through the front access grill, providing crucial personnel protection by creating an inward airflow barrier. This is complemented by a HEPA-filtered laminar downflow in the work zone, which secures product protection by delivering ISO Class 5 clean air directly to the work surface without recirculating potentially contaminated air within the cabinet. Additionally, the air is drawn through another HEPA filter before being exhausted, which safeguards the external environment from contamination. Unlike other Class II cabinet types, all air in a Type B2 cabinet is exhausted to the outside through a dedicated exhaust system, making it appropriate for applications involving volatile chemicals or radionuclides.
External Exhaust Requirements and Fail-Safe Operation
Unlike other Class II cabinets, the Type B2 model relies heavily on external infrastructure for proper function. It does not operate autonomously but requires integration with an external exhaust blower. This external blower is essential for maintaining the cabinet's functionality, as it pulls the inflow and exhaust air through the system. The cabinet's internal motor primarily draws room air through an opening at the top, pushing it downward through the supply HEPA filter toward the work zone.
The system's design ensures that the internal blower will cease forcing air downward if the external blower fails. This precaution prevents hazardous particles from being blown out toward the user, a critical safety feature in the event of exhaust system failure. This interdependency between the internal and external blowers underscores the importance of proper installation and commissioning in accordance with NSF/ANSI 49 performance standards.
Under regular operation, the air the internal blower introduces is combined with air entering through the front access opening. This mixture is then entirely pulled out by the external exhaust blower, ensuring no contaminated air is recirculated back into the work zone or the laboratory environment. Because 100% of cabinet air is exhausted, Type B2 biosafety cabinets are frequently selected when laboratory procedures involve trace amounts of toxic chemicals in conjunction with biological materials. Proper ductwork design and exhaust balance are critical to maintaining containment performance.
References
1. NSF International Standard / American National Standard NSF/ANSI 49 - 2019
Reference: NSF International. (2019).
Biosafety Cabinetry: Design, Construction, Performance, and Field Certification Informative Annex 1 (formerly Annex E).
Ann Arbor, MI: NSF International.
2. NSF/ANSI 49-2022: Biosafety Cabinets Design and Performance
Reference: NSF International. (2022).
Biosafety Cabinets Design and Performance. Ann Arbor, MI: NSF International.
3. CETA Application Guide CAG-007
Reference: Controlled Environment Testing Association (CETA) (2020)
Exhaust System Requirements of Class II Biosafety Cabinets. Raleigh, NC: CETA.