Article
Article
Biosafety Cabinet Window Sash Level


Biosafety Cabinets (BSCs) provide essential personal, product, and environmental protection in laboratory settings. These cabinets undergo rigorous certification to meet NSF/ANSI 49 or EN 12469 standards. However, improper operation can undermine these protections. One critical aspect is maintaining the correct window sash level to prevent potential contamination.
Window Sash's Airflow Impact

The window sash, a movable or fixed window on the front of the cabinet, protects workers from the active work area. A BSC's certification is based on the window sash positioned at specific heights due to its impact on downflow and inflow velocities. Industry standards typically set the workable window sash height at 8, 10, or 12 inches (203, 254, or 305 mm).
Proper Window Height Notification
Most cabinets include indicators showing where the window should be during work activities. Modern cabinets and some older models from the 1990s feature a window sash alarm to alert users if the sash is not aligned correctly. Before a BSC leaves the NuAire factory, it undergoes testing to balance airflow, ensuring the workable sash height is set at your requested level of 8, 10, or 12 inches (203, 254, or 305 mm). After installation, a professional will certify your cabinet at the designated window sash height.
Importance of Window Sash Positioning
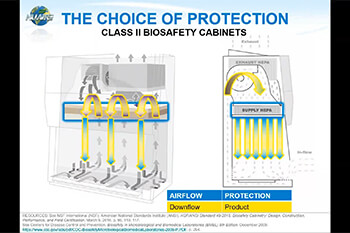
Proper window sash positioning is vital for the effective operation of biosafety cabinets. BSCs are designed to prevent contaminated air from entering both the work zone and the laboratory while minimizing cross-contamination within the work zone through unidirectional airflow. Achieving this requires maintaining a precise balance between inflow and downflow velocities.
Improper Airflow Balance

Airflow balance is compromised when the window sash is not at the certified working level. If the inflow velocity is too strong, contaminated air can enter the sterile work area, contaminating the work. Excessive downflow velocity can push contaminated air from the cabinet into the laboratory without proper filtering, creating turbulent air at the work surface and causing product contamination.
Potential Risks: Contaminated Air and Work Space
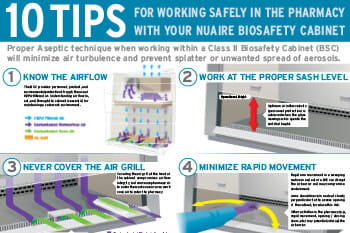
Unbalanced airflow velocities pose significant risks, especially when handling infectious materials. These imbalances can also disrupt controlled experimental conditions, such as those necessary for growing cell cultures. Proper window sash positioning promotes careful and precise interaction within the cabinet. The correct sash height allows workers to use smooth arm movements, minimizing the entry of room air into the cabinet. If the sash is positioned too high or too low, workers may have to reach excessively, churning the interior air and increasing the risk of contamination, splattering, and handling errors.